Cloud consulting services are being used by businesses of all sizes, regions, and industries. According to a RightScale poll, public and private cloud use has surged in the last year.
According to the poll, respondents are now embracing public cloud at 92 percent, up from 89 percent in 2017, and private cloud at a rate of 75 percent, up from 72 percent in 2017. As a result, 96 percent of respondents now say they use at least one public or private cloud.
According to Gartner, this trend will continue through 2020, when most firms have adopted cloud-first or cloud-only strategies. Lower operating expenses, improved time to market, stronger collaboration, and increased flexibility are all factors that have contributed to this shift.
The cloud is a fantastic method to run a business since it has many benefits and a few drawbacks.
[lwptoc]Before we delve into the benefits a company can get by using cloud infrastructure, let’s take a brief look at cloud computing and how enterprises can migrate to the cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?
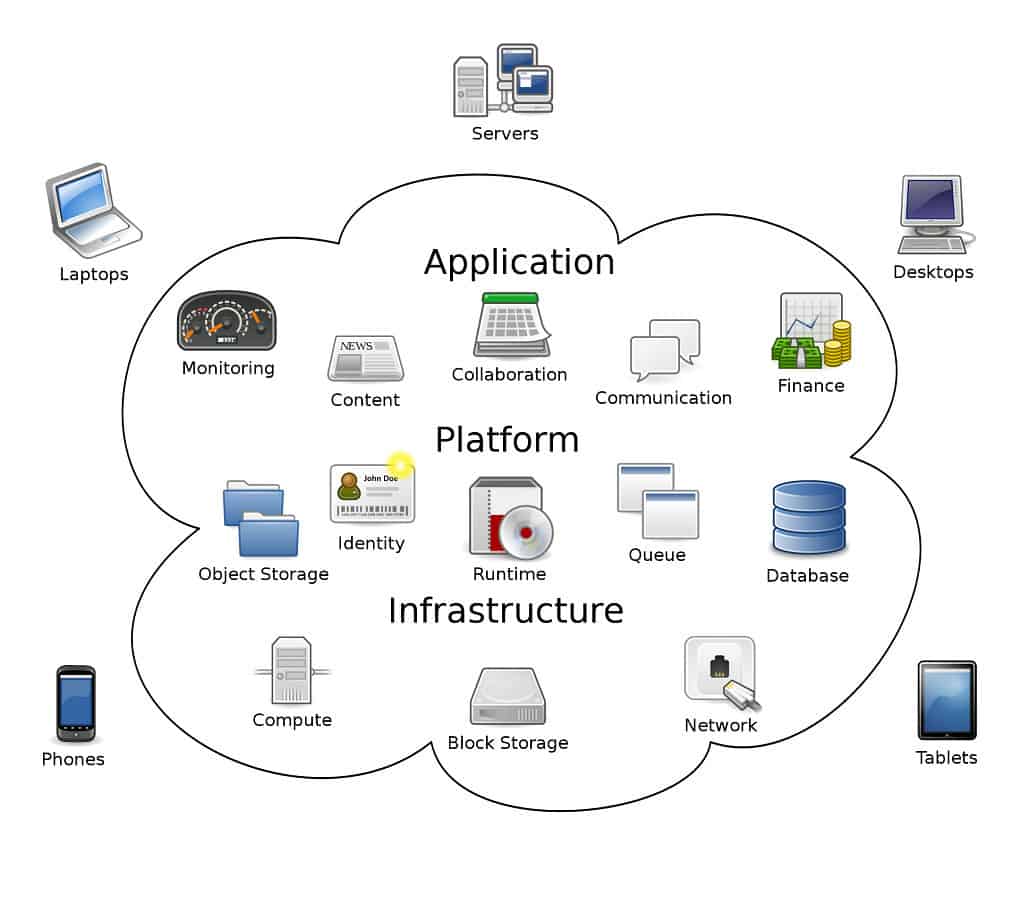
Cloud computing is a concept that refers to the utilization of network-delivered hardware and software. The phrase stems from using a cloud-shaped symbol that illustrates the abstraction of a rather complicated infrastructure that allows software, hardware, computing, and distant cloud consulting services to interact together.
Simply speaking, cloud computing is internet-based computing. People use software downloaded on a real computer or server to run applications or programs in their building. Cloud computing provides internet-based access to the same types of applications.
Cloud computing is built on the idea that the central processing takes place on a system that isn’t currently in use and that this machine is often remote. Remote servers store and process the data collected throughout this procedure. As a result, the cloud-accessing gadget does not have to work as hard.
Cloud servers free up memory and computing capacity on individual PCs by remotely hosting software, platforms, and databases. Using credentials provided by the cloud computing provider, users can safely access cloud consulting services.
Cloud Computing Benefits
Here’s a rundown of the primary advantages a company can expect from cloud infrastructure.
1. High Speed – Quick Deployment
The ability to create new cloud computing instances in a couple of seconds revolutionized software development agility and speed. Without relying on on-site hardware limits or lengthy procurement processes, developers may quickly test new ideas and construct application architecture.
2. Automatic Software Updates and Integration
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery rely on the fact that new software versions can be readily tested and deployed in the cloud environment, allowing for faster product innovation and the release of more features to end-users on a monthly, weekly, or even daily basis. Cloud environments also interface with specific DevOps tools and logging systems, making monitoring and detecting faults in production much more effortless.
3. Efficiency and Cost Reduction
You won’t have to spend a lot of money purchasing and maintaining equipment if you use cloud infrastructure. CAPEX and TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP ARE DRASTICALLY REDUCED (TCO). You don’t need to invest in hardware, infrastructure, utilities, or a massive data center to expand your firm. You don’t even need huge IT teams to run your cloud data center operations because you may use your cloud provider’s experience.
Downtime costs are also reduced by using the cloud. Because downtime is uncommon in cloud systems, you won’t have to waste time and money resolving potential downtime concerns.
4. Data Security
The security of a company’s data is one of its main priorities, regardless of its size or industry. Data breaches and other forms of cyber crime may wreak havoc on a company’s revenue, customer loyalty, and brand image.
Many advanced security mechanisms are available in the cloud, ensuring that data is stored and handled safely. Granular permissions and federated roles can limit access to sensitive data to only those employees who need it, lowering the attack surface for unscrupulous actors.
Baseline security measures, such as authentication, access control, and encryption, are implemented by cloud storage providers for their platforms and the data they process. Most businesses then complement these safeguards with additional security measures to strengthen cloud data security and restrict access to sensitive data in the cloud.
5. Scalability
Distinct businesses have different IT requirements; a major corporation with 1000+ people would not have the exact IT requirements as a small business. The cloud is an excellent solution because it allows businesses to scale up and down their IT departments efficiently and quickly in response to business needs.
Cloud-based solutions are appropriate for enterprises with fluctuating or escalating bandwidth requirements. You may quickly scale up your cloud capacity without having to invest in physical equipment as your business demands grow. This amount of adaptability can give cloud computing users a significant competitive advantage.
This scalability reduces the risks of internal operational problems and maintenance. With professional solutions and no upfront commitment, you have high-performance resources at your disposal. The cloud’s most significant advantage is undoubtedly its scalability.
6. Omnipresence
Cloud is omnipresent, and there is no way to avoid it. Its ubiquity enables quick access to functionality, data tracking, and transparency. It allows numerous users to work on the same project simultaneously without any issues.
Because of the cloud’s ubiquity, vital access to visible and traceable data is possible. Multiple people working in the cloud simultaneously is not a problem. As a result, a powerful network is established while costs are reduced. As a result, costs are reduced, and a stable work paradigm is also established.
7. Complete control
Businesses are frequently scrutinized when it comes to sluggish operations, data loss, and operational dysfunction. cloud computing services provides organizations with the necessary control over the company’s ongoing operations.
The Cloud gives users a bird’s eye perspective of the data, allowing them to track accessibility, usability, and deployability when it comes to sensitive data.
While it gives management control, it also simplifies work by compartmentalizing tasks per employee and giving them individual access to their particular responsibilities. This allows for a clear comprehension of the job to be completed and a clear path to task completion.
8. Flexibility
Focusing solely on the in-house IT infrastructure can result in system failure or inadequate execution. Low turnaround times and the inability to meet client needs can result from a lack of space optimization.
Low bandwidths are not a constraint in the cloud. It is more adaptable than traditional in-house technological infrastructure, allowing organizations to make last-minute adjustments while maintaining productivity.
The cloud platform is one of the most wanted because it allows you to make and execute swift business choices without worrying about the impact on your IT infrastructure.
9. Mobility
The cloud’s omnipresence highlights mobility as a key aspect. Companies may easily connect remotely via cloud connectivity on various devices such as smartphones, iPads, and laptops.
Remote access allows for short turnaround times, immediate solutions, and continuous connectivity. It’s ideal for freelancers, remote workers, and businesses with offices in various regions and industries.
This personifies convenience, and it’s no surprise that, according to IDC, businesses will spend over 3.5 million dollars on cloud software in 2021 alone.
10. Disaster Recovery
“Data loss” is the worst disaster a firm may face. On the other hand, the cloud serves as a storage location for backed-up data, allowing businesses to quickly and securely restore lost data. According to 65 percent of senior IT executives, security and regulatory risks are the biggest roadblocks to realizing the benefits of the cloud.
The cloud reduces the nearly 6 hours per week spent on technical issues, latencies to the home server, and other inconveniences. That’s the equivalent of a lost day! To improve this, bring in the cloud.
One of the key benefits of the cloud is disaster recovery, which ensures that even government officials have updated their cloud. The cloud is presently used by 50% of US federal entities.
Conclusion
Every year, the number of people using cloud computing grows, and it’s easy to see why. Enterprises understand the advantages of cloud computing and how they affect production, collaboration, security, and income.
An organization can avoid many issues that affect enterprises that rely on on-premises technology by employing a cloud-based solution.