For a long time, the Windows command prompt has been an integral part of the Windows operating system. Some CMD commands are so useful and simple to use that even novice users regard the Windows command prompt as an essential component of the operating system. It’s always rumored that it’ll be phased out at some point, but that’s unlikely to happen anytime soon. The following are 20 of the most useful CMD commands to know if you want more control over your Windows PC.
20 Best CMD Commands
CMD Commands that every Windows user should be aware of.
[lwptoc]1. FC: File Compare
When files are changed over time, it can be difficult to remember what the differences were between versions. You might not realize that a CMD command allows you to compare files and see all differences, but it’s true.
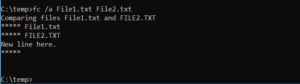
The FC command compares two files, either ASCII or binary, and outputs a list of any differences found.
1- Fc /a File1.txt File2.txt will compare two ASCII files.
2- Fc /b Picture1.jpg Picture2.jpg will make a binary comparison of two images.
2. ASSOC: Fix File Associations
The ASSOC command is one of the most powerful tools in the CMD command library.
Certain file extensions are associated with specific programs on your computer. For example, when you double-click a PDF file, your computer knows to open Adobe, and when you double-click a DOC file, it knows to open Microsoft Word.
By typing ASSOC in the command window, you can view all of the file associations that your computer is aware of. In addition, you’ll see the file extension and the program with which it’s associated.
You can change the association by typing assoc.doc=Word.Document.8.
3. NETSTAT: Network Statistics
Concerned that you may have malware running on your computer that is connecting to the internet without your knowledge?
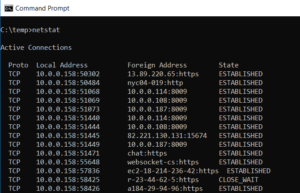
Well, You can get a list of all active TCP connections from your computer by running the NETSTAT command in the command prompt.
4. IPCONFIG: IP Configuration
Network troubleshooting is never easy, but IPCONFIG is a command that makes it much easier.
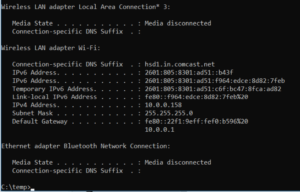
This command, when entered into the CMD command prompt, returns detailed information about your current network adapter connection, including:
1- Current IP Address
2- Subnet Mask
3- Default Gateway IP
4- Current domain
This information can assist you in troubleshooting router issues and other network adapter connection issues.
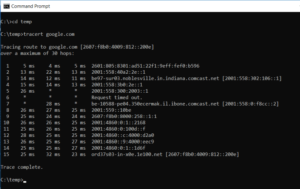
5. TRACERT: Trace Route
TRACERT is an enthralling Windows Command to work with. If you’ve ever wondered what path your internet traffic takes from your browser to a remote system, such as Google servers, you can use TRACERT to find out.
The command stands for “Trace Route,” and it sends packets to a remote destination (server or website) and returns the following information:
1- Number of hops (intermediate servers) before getting to the destination
2- Time it takes to get to each hop
3- The IP and sometimes the name of each hop
TRACERT can show you how the paths of your internet requests change depending on where you access the internet. It also aids in troubleshooting a problematic router or switch on a local network.
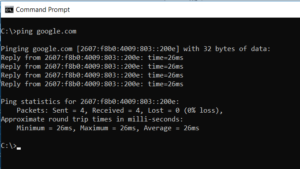
6. PING: Send Test Packets
The PING command is an IT Analyst’s best friend. This command sends test packets to the target system over the network.
Well, The PING command can be used to see if your computer can connect to another computer, a server, or even a website. It can aid in the detection of network disconnections. It also provides packet transit time in milliseconds, which reveals a bad network connection.
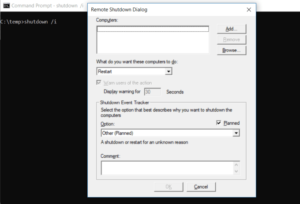
7. SHUTDOWN: Turn Off Computer
The SHUTDOWN command is a fairly versatile command that allows you to shut down the computer while controlling its behavior. For example, after patches have been applied to a computer system, it is commonly used as a scheduled task or as part of an IT batch job.
Well, Typing shutdown /i from the command prompt will restart a shutdown, but it will rely on a GUI to give the user the option of restarting or performing a full shutdown. If you don’t want the GUI to appear, simply use the shutdown /s command.
There’s a long list of other parameters you can use to log off, hibernate, restart, and more. To see them all, type shutdown without any arguments.
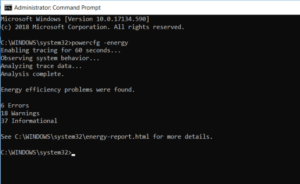
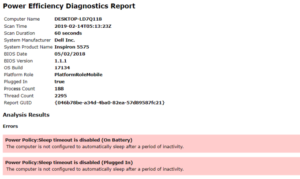
8. POWERCFG: Power Configuration
Are you frustrated by how quickly your laptop appears to run power? It’s possible that your power settings are set to be as efficient as possible. Well, A Windows CMD command called POWERCFG (power configuration) can be useful. To obtain a complete power efficiency report, run the command prompt as an administrator and type powercfg – energy.
The process can take up to a minute, but when it’s finished, you’ll see if there are any warnings or errors that can help you improve your system’s power efficiency.
View the energy-report.html file for more information on the errors and warnings.
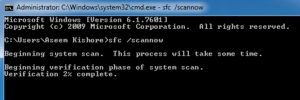
9. SFC: System File Checker
If you suspect that a virus or other software has corrupted your core system files, there is a Windows command that can scan those files and ensure their integrity.
You must run CMD as administrator (right-click and choose Run as Administrator). SFC /SCANNOW verifies the integrity of all protected system files. If a problem is discovered, the files will be repaired using previously backed-up system files.
The SFC command also lets you to:
1- /VERIFYONLY: Check the integrity but don’t repair the files.
2- /SCANFILE: Scan the integrity of specific files and fix if corrupted.
3- /VERIFYFILE: Verify the integrity of specific files but don’t repair them.
4- /OFFBOOTDIR: Use this to do repairs on an offline boot directory.
5- /OFFWINDIR: Use this to do repairs on an offline Windows directory.
6- /OFFLOGFILE: Specify a path to save a log file with scan results.
Give enough time for the scan, which can last up to 10 or 15 minutes.
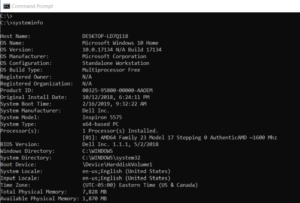
10. SYSTEMINFO: System Information
The SYSTEMINFO command can tell you what brand of network card you have, as well as processor details and the exact version of your Windows operating system.
This command polls your system and retrieves the most critical system information. It presents the information in a clear and easy-to-read format.
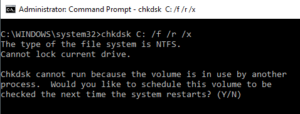
11. CHKDSK: Check Disk
Meanwhile, the SFC command only checks the integrity of core system files; the CHKDSK command can scan an entire drive.
Well, To check the C: drive and repair any issues, open a command window as an administrator and type CHKDSK /f C:.
This command looks for the following things:
- File fragmentation
- Disk errors
- Bad sectors
Also, The command can fix any disk errors (if possible). When the command is finished, you’ll see the scan’s status and the actions that were taken.
12. NET USE: Map drives
Well, If you want to map a new drive, open File Explorer, right-click This PC, and select the Map Network Drive wizard. However, you can accomplish the same thing with a single command string by using the NET USE command.
For example, if you’ve a shared folder called \\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE\ on a computer on your network, you can map it as your own Z: drive by typing the command:
:- Net use Z: “\\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE”/persistent:yes
The persistent switch instructs your computer that you want this drive remapped every time you log in.
13. ATTRIB: Change File Attributes
Well, In Windows, you can change file attributes by right-clicking on a file and selecting the appropriate property to change. Instead of searching for the file attribute, use the ATTRIB command to set the file attributes.
For instance, if you type: ATTRIB +R +H C:\temp\File1.bat, it’ll set File1.bat as a hidden, read-only file.
When it is successful, there is no response, so unless you see an error message, the command was successful.
14. SCHTASKS: Schedule Tasks
For creating scheduled tasks, Windows includes a wizard. For instance, suppose you have a BAT file on C:\temp that you want to run every day at noon.
To configure this, you’d need to go through the Scheduled Task wizard. You can set it up with a single SCHTASKS command.
:- SCHTASKS /Create /SC HOURLY /MO 12 /TR Example /TN c:\temp\File1.bat
The scheduled switch accepts minute, hourly, daily, and monthly arguments. The frequency is then specified using the /MO command.
If you typed the command correctly, you should receive the response SUCCESS: The scheduled task “Example” has been successfully created.
Other Windows CMD Commands
As you can see, if you know the right commands, you can do some very powerful and useful things with the Windows command prompt.
Believe it or not, there are still more commands that will give you the ability to do things you probably never realized you could do just by typing a simple command.
COLOR: Change the command prompt window’s background color.
BITSADMIN: Start upload and download jobs over a network or the internet, and monitor the status of those file transfers.
FIND/FINDSTR: Find strings within ASCII files.
COMP: Compare the contents of the two files to see if there are any differences.
TITLE: Change the command prompt window’s title.
PROMPT: Well, Change the command prompt from C:\> to something else.
ROBOCOPY: A powerful file copy utility that comes standard with Windows.
If you want to learn more, Microsoft provides a complete list of all of the Windows CMD commands included in the most recent version of the Windows operating system.